About South Korea
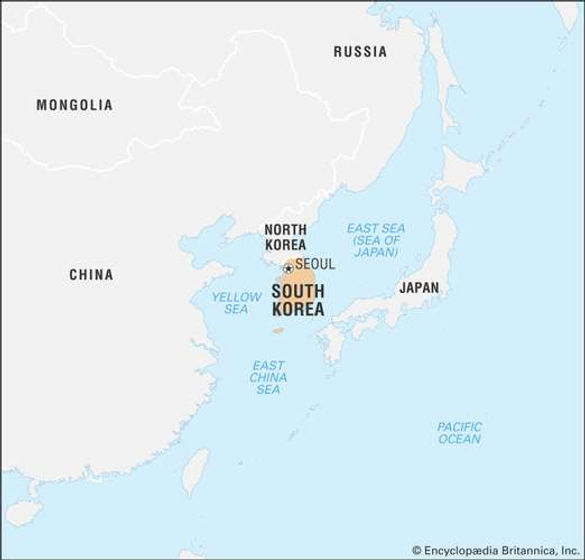
South Korea is a country in East Asia, more specifically the southern portion of the Korean Peninsula. It is bordered by the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea) to the north. To the East Sea along the east, the East China Sea to the south, and the Yellow Sea to the west.
South Korea faces North Korea across a demilitarized zone (DMZ) 2.5 miles (4 km) wide that was established by the terms of the 1953 armistice that ended fighting in the Korean War (1950–1953). The DMZ, which runs for about 150 miles (240 km), constitutes the 1953 military cease-fire line and roughly follows latitude 38° N (the 38th parallel) from the mouth of the Han River on the west coast of the Korean peninsula to a little south of the North Korean town of Kosŏng on the east coast (Hahn & Im, 2020).
South Korea's population consists of 51,966,000 on a 2019 estimate and is projected to increase to 53,784,000 by 2030 (Hahn & Im, 2020). Amazingly the population spans over just 37,491 sq mi (Hahn & Im, 2020). In addition, Korea is land to two volcanic islands - Jeju, which is off of the peninsula's southernmost tip, and a small-scale lava plateau in Kangwon province. (Hahn & Im, 2020). Korea also lays claim to Dok Island.
Korea's population has more than doubled over the second half of the 20th century. From 1960, however, birth rates decreased rapidly, and the population growth rate was almost negligible by the beginning of the 21st century. During the same period, mortality rates also slowed, reflecting an overall increase in standards of living (Hahn & Im, 2020).
Urban populations have rapidly increased while rurals areas continue to depopulate making it demographic issue. More than half of the population live in the country's seven largest cities, making these areas very dense amidst the decreasing birth rates.
Korea has freedom to religion. There is no national religion. Many Koreans do not affiliate with a religion. Approximately one-fourth of the population affiliate with Christianity, with Protestants, independent Christians, and Roman Catholics the largest groups. Less than one-sixth of the population is Buddhist (Hahn & Im, 2020).
Less than a quarter of the land is cultivated. With the decreasing population and age of the rural areas, there is a farm-labor shortage. However, more recently productivity has been improving as greater emphasis has been given to mechanization, specialization, and commercialization.
Rice makes the most important crop in Korea. Barely secondary to pork, beef, and milk. Other major agricultural products include citrus fruits, persimmons, and cabbage (Hahn & Im, 2020).



